Blog
Valve Systems for Petrochemical Processing

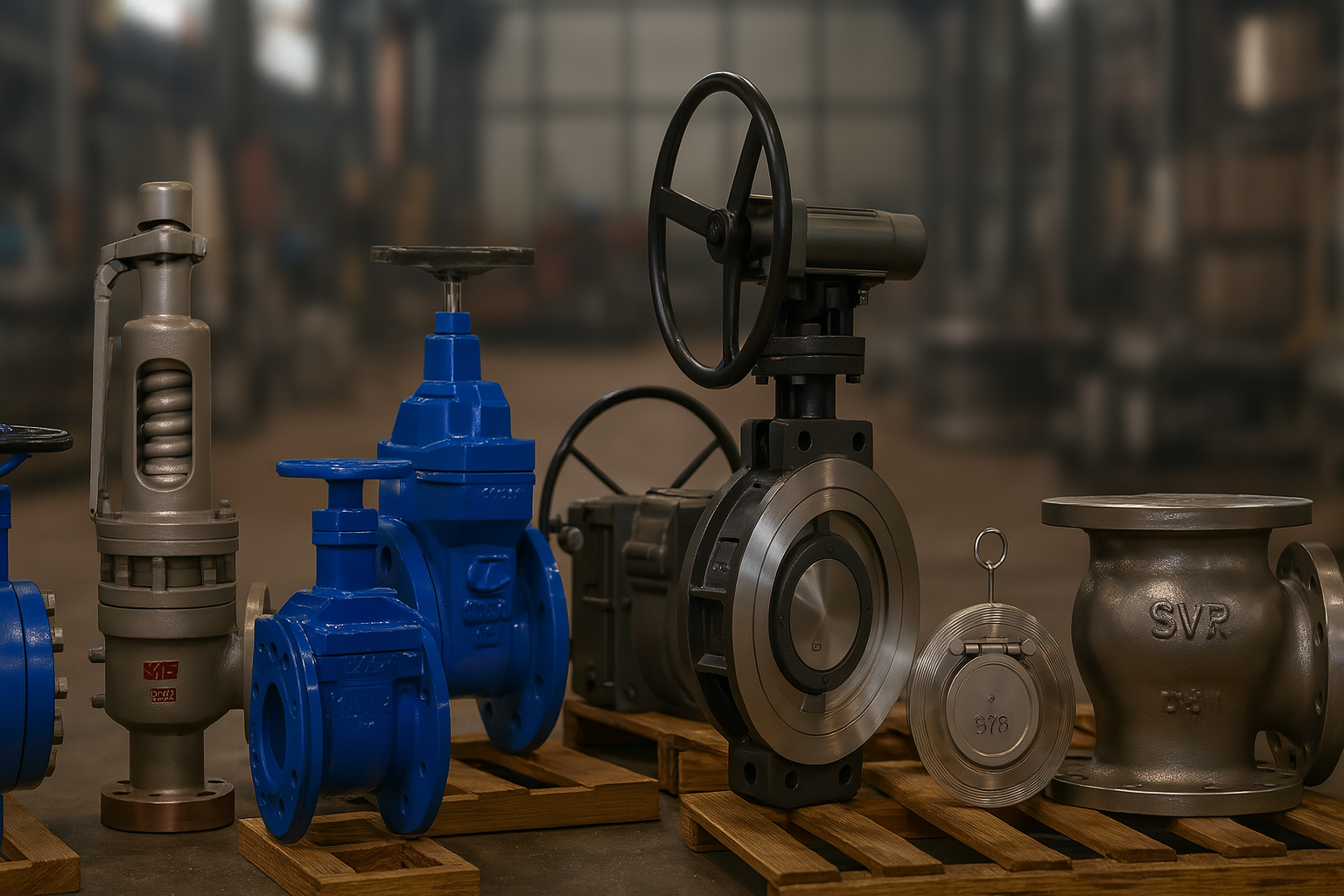
Industrial valves for petrochemical processing control, isolate, and regulate hydrocarbons, gases, steam, and corrosive chemicals under high pressure and temperature conditions. These valves must comply with API, ASME, and fire-safe standards to ensure operational safety, emission control, and continuous plant performance.
Valves provide the basis of operational safety and process control in petrochemical facilities. Valves are required at every stage from raw hydrocarbon processing to finished chemical manufacture to start, stop, route, or control flow under harsh operating conditions. High pressures, increased temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and volatile gases are usual conditions in these environments, leaving little room for component failure.
The significance of Valve Selection in Petrochemical Factories
Operating around the clock, petrochemical plants regularly deal with dangerous liquids that pose fire, explosion, and environmental hazards. Valves are essential safety parts rather than auxiliary apparatus in these situations.
A correctly chosen valve has to be able of:
- Quickly separating process units under unusual or emergency circumstances
- Preserving consistent flow, pressure, and temperature across operations
- Safeguard pumps, compressors, and rotating equipment against backflow.
- Advocating automatic control in columns, reactors, and separators
- Working dependably during fire exposure and fulfilling emission standards
Choosing the wrong valve can threaten process stability, quicken equipment deterioration, and raise the possibility of unscheduled shutdowns or safety events.
For On–Off Isolation: Gate Valves
Basic operating purpose: total shutdown
Where open position calls for unrestricted flow and shut tight isolation is absolutely necessary, gate valves find extensive application. Their straight-through flow path fits them for high-pressure hydrocarbon applications.
Among the typical uses are:
- Lines for crude transfer and feedstock
- High Temperature Process Piping
- Key isolating points inside process units
Factors to consider when designing:
- Made for entirely open or completely closed operation
- Throttle service might cause fast seat and gate deterioration.
- Usually set for greater pressure levels
Engineering note: Commonly specified for critical hydrocarbon separation are gate valves made to API 600 or API 602.
Control Flow Globe Valves
Main objective: Regulation
Where precise flow regulation is needed, globe valves are favored. Their internal geometry enables exact modulation of flow even under fluctuating pressure conditions.
Typical services are:
- Systems for steam and condensate
- Lines for flow and pressure management
- Chemical injection and dose applications
Design Factor:
- More pressure drop than isolation valves
- Good for continuous use
- Offers constant and stable control precision
Engineering Note: Globe valves are ideal for controlled services rather than for long-distance pipeline transport.
Quick and dependable ball valve shutdown
Main utility: rapid isolation
Where fast operation and tight closing are needed, ball valves are frequently employed. Their quarter-turn system qualifies them for use in automated as well as hand systems since it allows for rapid response.
Common services comprise:
- Dissemination and transportation of hydrocarbons
- handling systems for gas
- Applications for emergency termination
Design ideas:
- Low driving torque
- Effective sealing even after long inactivity periods
- Constructions resistant to fire now accessible
Engineering note: Often specified for safety-related isolation purposes, API 6D compliant ball valves are
Butterfly Valves in Big Pipeline Networks
Main purpose: compact flow regulation
Large pipe sizes with weight and space limitations that affect design selection frequently use butterfly valves. For moderate pressure services, they offer a cheap solution.
Typical services comprise:
- Cooling water systems of circulation
- Auxiliary and utilitarian facilities
- Choose lines of operation.
Types of designs:
- Double-offset systems for better sealing
- High-temperature applications using triple-offset metal-seated designs
Triple-offset butterfly valves are favored in situations needing high pressure capability and close shutoff.
Backflow Check Valves
Principal use: Automated flow directional regulation
Check valves preserve process integrity and safeguard vital equipment by preventing reverse flow without outside activation.
Regular installation locations are:
- Lines that pump discharge
- outlets for compressors
- Piping with respect to safety
Among popular patterns are:
- swing check valves
- Lift check valves
- Dual-plate wafer check valves
Dual-plate designs are ideal for small pipe systems since they help to reduce pressure surges.
Control Valves in Automatic Petrochemical Processes
Basic Use: Stability in Continuous Processes
Automated petrochemical systems depend on control valves, which change process parameters depending on signals received from instrumentation and control systems.
Main applications include:
- Control of reactor feed
- Control of pressure and temperature
- Correct columns and separators
Alternatives for actuating include:
- Pneumatic actuators
- Electric actuators
Engineering note: Stable and sensitive control performance depends on proper Cv sizing and complete compatibility with PLC or DCS systems.
Material issues for petrochemical valves
Material selection under severe operating circumstances is very important for the valve’s longevity, safety, and service life.
Among the typical material choices are:
- Carbon steel for typical hydrocarbon applications
- Stainless steel for duties involving elevated temperatures or corrosion
- High-pressure and high-temperature alloy steel
- Duplex and super duplex stainless steels suitable for chloride-rich situations
- For highly corrosive chemical services, constructions lined with PTFE
Valve use over sections of the petrochemical process
- Gate, ball, and control valves: crude and feed preparation.
- Cracking and remodeling mechanisms: Globe, check, and control valves
- Unit polymer processing: ball, butterfly, and aligned valves
- Storage and distribution systems: butterfly, ball, and gate valves
- Valve checks, gate, and butterfly utility systems
Codes, standards, and safety demands
To guarantee safe and dependable functioning, valves used in petrochemical applications must meet exacting global norms, including:
- Pressure-temperature ratings under ASME B16.34
- Standards for valve design, testing, and performance derived from APIs
- Fire safety credentials for emergency conditions
- Guidelines for emission control for environmental conformance
Following these standards guarantees consistent valve performance across the plant life cycle.
Backing Petrochemical and EPC Initiatives
Middle East Valve assists EPC contractors and plant operators by:
- Valves made to internationally approved standards.
- Materials available for harsh process circumstances
- Automation and safety systems call for solutions.
- Technical help during project execution
Delivering dependable valve solutions consistent with project specifications, operational safety requirements, and long-term plant performance is still our main aim.

