- Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Pneumatic Angle Control Valve
- 3 Way pneumatic Diaphragm Control Valve
- 3 Way Converging and Diverging Control Valve
- Fluorine Lined Single Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Cage Control Valve
- Pneumatic Double Seat Control Valve
- Pneumatic Single Seat Globe Control Valve
- Pneumatic Flow Control Valve
- Pneumatic Sleeve Type Control Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Globe Type Control Valve
- Electric Actuated Control Valve
- Pneumatic Control Valve
- Cryogenic Valve
- Pressure Reducing Valve
- Safety Valve
- Check Valve
- Gate Valve
- Butterfly Valve
- Globe Valve
- Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Valve
- Electric Actuated Ball Valve
- Electric Actuated Butterfly Valve
- Electric Actuated Gate Valve
- Electric Actuated Globe Valve
- Pneumatic Actuated Valve
- Plunger Valve
- Strainers
- Steam Trap
- Knife Gate Valve
- Speciality Valve
- Alloy 20 Valve
- Duplex Valve
- Super Duplex Valve
- Hastelloy C276/B3 Valve
- Aluminium Bronze Valve
- Titanium Valve
- Bronze Valve
- Monel Valve
- Triple Duty Valve
- Suction Diffuser
- Diaphragm Valve
- Plug Valve
- Foot Valve
- Air Release Valve
- Surge Anticipator Valve
- Needle Valve
- Balancing Valve
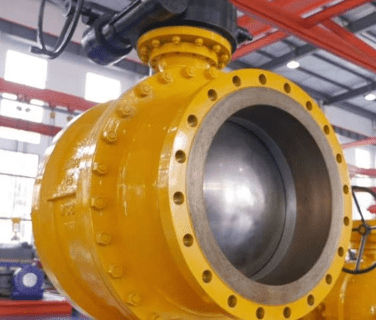
Casting Trunnion Ball Valve
Middleeast Valve is the leading Casting Trunnion Ball Valve Supplier in Saudi Arabia that provide high performance valve of high quality to fulfill the strict requirement of industrial process. Our trunnion ball valve are produced with utmost care to deliver efficient and reliable valve for liquid and gas flow control in critical application. We are delighted to provide valves to assure safety, durability, and high performance in industries.
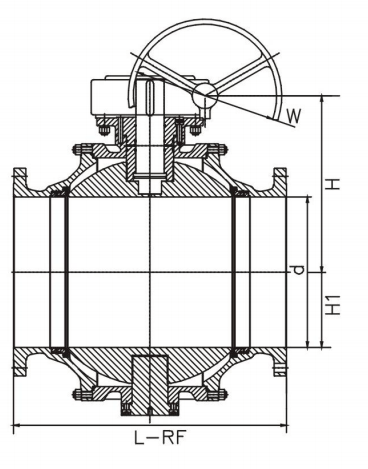
Key Elements of a Casting Trunnion Ball Valve
- Body: Made of strong casting material, ensuring the strength of valve under extreme condition.
- Trunnion-Mounted Ball: The ball rest on top and bottom trunnion providing stability and reducing stress on the ball when in operation.
- Stem: Connect the ball to the actuator, allowing for smooth movement of the valve.
- Seat: The sealing face that ensures leak-tight shut-off when the valve is closed.
- End Connections: Valve inlet and outlet, which are to be connected directly to the pipeline.
Working Mechanism
The Casting Trunnion Ball Valve operates by rotating the ball within the valve body. When the valve is opened, the ball hole is aligned with the pipeline in order to allow the fluid passage through it. The ball will be rotated 90 degrees to block the flow while in a closed position. The ball and trunnion-mounting configuration enable the valve to operate smoothly under pressure, providing more flow control while maintaining low friction.
Advantages of Casting Trunnion Ball Valve
- High Temperature and Pressure Tolerance: Ideal for extreme conditions due to its heavy-duty construction.
- Less Leakage: Trunnion-mounted reduces risk of leakage and hence is dependable.
- Longevity: Made from high-grade casting materials to ensure long service life.
- Smooth Operation: Trunnion ball mechanism provides smooth, low-torque operation.
- Multi-Application: Ideal for application in multiple industries, such as oil and gas and chemical processing.
Applications
- Oil and Gas: Upstream, midstream, and downstream processes.
- Petrochemicals: Refining plants, chemical processing facilities.
- Power Generation: Boilers for treating steam, water, and other fluids.
- Water and Wastewater: Utility water treatment and distribution networks.
- Process Industries: Numerous manufacturing processes and industrial activities.
- Mining: Treating abrasive materials and slurries.